Anne Reinarz Durham University
Outline
Outline
- Introductory remarks
- Network overview and its components
- Network protocol
- Physical media
- Network security
Introductory Remarks
Lecturer:
Introductory Remarks
Practicals:
- Demonstrators will be present to assist you in the labs
- Currently planned to take place in person
- Labs described on DUO (weeks 2,4,6,8, and 10)
Introductory Remarks
Assessment:
- 100% coursework
- Hand out date: Week 4 (Monday 26th October)
- Hand in date: Term 2 (Monday 11th February)
Introductory Remarks
- All lectures will take place via zoom
- Please remain muted unless you want to ask a question
- Questions can also be typed in the chat
- Office hours can be arranged by email
Course Outline
- Network standards and basic network architecture
- Client-server and P2P (Peer to Peer) networks
- Sockets and socket programming: TCP and UDP
- Routing algorithms
- Error detection and recovery
- Digital modulation approaches
Emphasis on:
- How networks function
- How to write network applications
Reading Material
 </img>
</img> </img>
</img>What are the main components and devices?
--- ## The Internet: "nuts and bolts" view - Billions of connected computing devices: </img>
- Hosts = end systems
- Running network apps
---
## The Internet: "nuts and bolts" view
</img>
- Hosts = end systems
- Running network apps
---
## The Internet: "nuts and bolts" view
 </img>
- Communication links
- Fiber, copper, radio, satellite
- Transmission rate: bandwidth
- Packet switches: forward packets (chunks of data)
- Routers and switches
</img>
- Communication links
- Fiber, copper, radio, satellite
- Transmission rate: bandwidth
- Packet switches: forward packets (chunks of data)
- Routers and switches
Protocols define the format and order of messages sent and received among network entities, and actions taken on message transmission and receipt.
- specific messages sent - specific actions taken when messages received, or upon other events --- # What’s a protocol?
### Human protocols:
- “what’s the time?”
- “I have a question”
- Introductions...
### Network protocols:
- Machines rather than humans
- All communication activity in Internet governed by protocols
---
# Protocol Examples
- a human protocol and a computer network protocol:
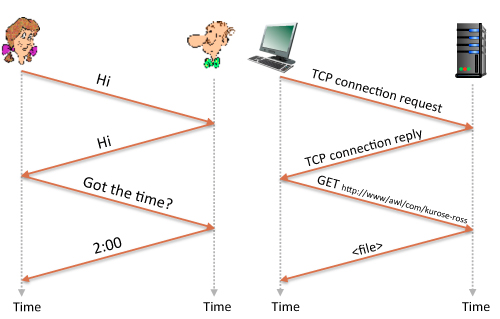 </src>
---
# Access network:
---
# Access network:
## digital subscriber line (DSL)
</src>
---
# Access network:
---
# Access network:
## digital subscriber line (DSL)
 </img>
---
# Access network:
## digital subscriber line (DSL)
- Use existing telephone line to central office DSLAM
- data over DSL phone line goes to Internet
- voice over DSL phone line goes to telephone net
- Asymmetric access: downstream and upstream rates are different
- < 2.5 Mbps upstream transmission rate (typically < 1 Mbps)
- < 24 Mbps downstream transmission rate (typically < 10 Mbps)
---
# Access network:
## cable network
</img>
---
# Access network:
## digital subscriber line (DSL)
- Use existing telephone line to central office DSLAM
- data over DSL phone line goes to Internet
- voice over DSL phone line goes to telephone net
- Asymmetric access: downstream and upstream rates are different
- < 2.5 Mbps upstream transmission rate (typically < 1 Mbps)
- < 24 Mbps downstream transmission rate (typically < 10 Mbps)
---
# Access network:
## cable network
 </img>
---
# Access network:
## cable network
- HFC: hybrid fiber coax
- asymmetric: up to 42.8 Mbps downstream transmission rate, 30.7 Mbps upstream transmission rate
- Network of cable, fiber attaches homes to ISP router
- homes share access network to cable headend
- unlike DSL, which has dedicated access to central office
---
# Enterprise access networks:
## Ethernet
</img>
---
# Access network:
## cable network
- HFC: hybrid fiber coax
- asymmetric: up to 42.8 Mbps downstream transmission rate, 30.7 Mbps upstream transmission rate
- Network of cable, fiber attaches homes to ISP router
- homes share access network to cable headend
- unlike DSL, which has dedicated access to central office
---
# Enterprise access networks:
## Ethernet
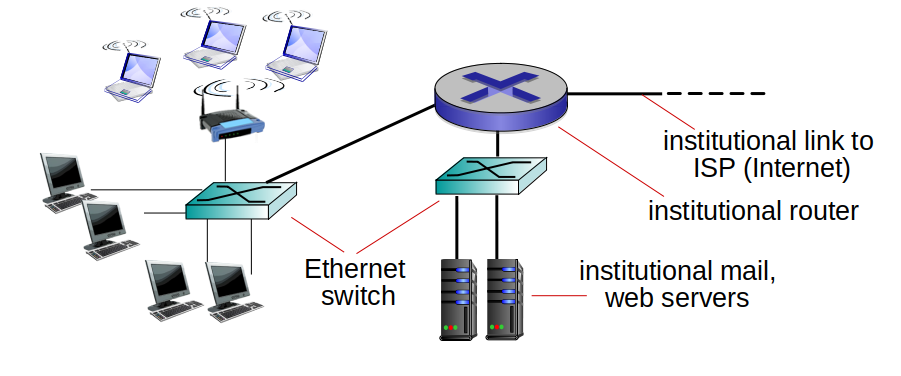 </img>
---
# Enterprise access networks:
## Ethernet
- Widely used in companies, universities, etc.
- 10 Mbps, 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 10Gbps transmission rates
- Today, end systems typically connected by Ethernet switches
---
# Access network:
## home network
</img>
---
# Enterprise access networks:
## Ethernet
- Widely used in companies, universities, etc.
- 10 Mbps, 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 10Gbps transmission rates
- Today, end systems typically connected by Ethernet switches
---
# Access network:
## home network
 </img>
---
# Wireless access networks
- Shared wireless access network connects end system to router
- via base station, aka “access point”
---
# Wireless access networks
</img>
---
# Wireless access networks
- Shared wireless access network connects end system to router
- via base station, aka “access point”
---
# Wireless access networks
 </img>
- Wireless LANs:
- Within building (~100 ft.)
- 802.11 (WiFi)
- 54~1300 Mbps transmission rate
</img>
- Wireless LANs:
- Within building (~100 ft.)
- 802.11 (WiFi)
- 54~1300 Mbps transmission rate
 </img>
- Wide-area wireless access
- Provided by telco (mobile) operator, 10’s of km
- Between 1 and 10 Mbps
- 3G, 4G, LTE (“Long Term Evolution”), 5G
---
# Internet of Things (IoT)
</img>
- Wide-area wireless access
- Provided by telco (mobile) operator, 10’s of km
- Between 1 and 10 Mbps
- 3G, 4G, LTE (“Long Term Evolution”), 5G
---
# Internet of Things (IoT)
 </img>
Link
---
# Physical Media
---
# Physical Media
- Bit
- propagates between transmitter/receiver pairs
- Physical link
- what lies between transmitter & receiver
- Guided media
- signals propagate in solid media: copper, fiber, coax
- Unguided media
- signals propagate freely, e.g. radio
---
# Physical Media
### Types of physical media:
- Twisted pair (TP)
- Copper wire
- Coaxial cable
- Fibre optic
- Terrestrial radio spectrum
- Satellite radio spectrum
---
# Physical Media
</img>
Link
---
# Physical Media
---
# Physical Media
- Bit
- propagates between transmitter/receiver pairs
- Physical link
- what lies between transmitter & receiver
- Guided media
- signals propagate in solid media: copper, fiber, coax
- Unguided media
- signals propagate freely, e.g. radio
---
# Physical Media
### Types of physical media:
- Twisted pair (TP)
- Copper wire
- Coaxial cable
- Fibre optic
- Terrestrial radio spectrum
- Satellite radio spectrum
---
# Physical Media
 </src>
## Twisted pair:
- Two insulated copper wires
- Category 5: 10 Mbps, 1 Gbps Ethernet
- Category 6: 10 Gbps
</src>
## Twisted pair:
- Two insulated copper wires
- Category 5: 10 Mbps, 1 Gbps Ethernet
- Category 6: 10 Gbps
 </img>
## Coaxial cable:
- Two concentric copper conductors
- Can achieve high data transmission rates
---
# Physical Media
</img>
## Coaxial cable:
- Two concentric copper conductors
- Can achieve high data transmission rates
---
# Physical Media
 </src>
### Fiber optic cable:
- Glass fibre carrying light pulses representing bits
- High-speed operation:
- High-speed point-to-point transmission (e.g., 10’s-100’s Gbps transmission rate)
- Low error rate:
- Repeaters spaced far apart
- Immune to electromagnetic noise
</src>
### Fiber optic cable:
- Glass fibre carrying light pulses representing bits
- High-speed operation:
- High-speed point-to-point transmission (e.g., 10’s-100’s Gbps transmission rate)
- Low error rate:
- Repeaters spaced far apart
- Immune to electromagnetic noise
---
# Physical Media
### Radio
 </src>
---
# Access network:
---
# Access network:
## digital subscriber line (DSL)
</src>
---
# Access network:
---
# Access network:
## digital subscriber line (DSL)
 </img>
---
# Access network:
## digital subscriber line (DSL)
- Use existing telephone line to central office DSLAM
- data over DSL phone line goes to Internet
- voice over DSL phone line goes to telephone net
- Asymmetric access: downstream and upstream rates are different
- < 2.5 Mbps upstream transmission rate (typically < 1 Mbps)
- < 24 Mbps downstream transmission rate (typically < 10 Mbps)
---
# Access network:
## cable network
</img>
---
# Access network:
## digital subscriber line (DSL)
- Use existing telephone line to central office DSLAM
- data over DSL phone line goes to Internet
- voice over DSL phone line goes to telephone net
- Asymmetric access: downstream and upstream rates are different
- < 2.5 Mbps upstream transmission rate (typically < 1 Mbps)
- < 24 Mbps downstream transmission rate (typically < 10 Mbps)
---
# Access network:
## cable network
 </img>
---
# Access network:
## cable network
- HFC: hybrid fiber coax
- asymmetric: up to 42.8 Mbps downstream transmission rate, 30.7 Mbps upstream transmission rate
- Network of cable, fiber attaches homes to ISP router
- homes share access network to cable headend
- unlike DSL, which has dedicated access to central office
---
# Enterprise access networks:
## Ethernet
</img>
---
# Access network:
## cable network
- HFC: hybrid fiber coax
- asymmetric: up to 42.8 Mbps downstream transmission rate, 30.7 Mbps upstream transmission rate
- Network of cable, fiber attaches homes to ISP router
- homes share access network to cable headend
- unlike DSL, which has dedicated access to central office
---
# Enterprise access networks:
## Ethernet
 </img>
---
# Enterprise access networks:
## Ethernet
- Widely used in companies, universities, etc.
- 10 Mbps, 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 10Gbps transmission rates
- Today, end systems typically connected by Ethernet switches
---
# Access network:
## home network
</img>
---
# Enterprise access networks:
## Ethernet
- Widely used in companies, universities, etc.
- 10 Mbps, 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 10Gbps transmission rates
- Today, end systems typically connected by Ethernet switches
---
# Access network:
## home network
 </img>
---
# Wireless access networks
- Shared wireless access network connects end system to router
- via base station, aka “access point”
---
# Wireless access networks
</img>
---
# Wireless access networks
- Shared wireless access network connects end system to router
- via base station, aka “access point”
---
# Wireless access networks
 </img>
- Wireless LANs:
- Within building (~100 ft.)
- 802.11 (WiFi)
- 54~1300 Mbps transmission rate
</img>
- Wireless LANs:
- Within building (~100 ft.)
- 802.11 (WiFi)
- 54~1300 Mbps transmission rate
 </img>
- Wide-area wireless access
- Provided by telco (mobile) operator, 10’s of km
- Between 1 and 10 Mbps
- 3G, 4G, LTE (“Long Term Evolution”), 5G
</img>
- Wide-area wireless access
- Provided by telco (mobile) operator, 10’s of km
- Between 1 and 10 Mbps
- 3G, 4G, LTE (“Long Term Evolution”), 5G
 </img>
Link
---
# Physical Media
---
# Physical Media
- Bit
- propagates between transmitter/receiver pairs
- Physical link
- what lies between transmitter & receiver
- Guided media
- signals propagate in solid media: copper, fiber, coax
- Unguided media
- signals propagate freely, e.g. radio
---
# Physical Media
### Types of physical media:
- Twisted pair (TP)
- Copper wire
- Coaxial cable
- Fibre optic
- Terrestrial radio spectrum
- Satellite radio spectrum
---
# Physical Media
</img>
Link
---
# Physical Media
---
# Physical Media
- Bit
- propagates between transmitter/receiver pairs
- Physical link
- what lies between transmitter & receiver
- Guided media
- signals propagate in solid media: copper, fiber, coax
- Unguided media
- signals propagate freely, e.g. radio
---
# Physical Media
### Types of physical media:
- Twisted pair (TP)
- Copper wire
- Coaxial cable
- Fibre optic
- Terrestrial radio spectrum
- Satellite radio spectrum
---
# Physical Media
 </src>
## Twisted pair:
- Two insulated copper wires
- Category 5: 10 Mbps, 1 Gbps Ethernet
- Category 6: 10 Gbps
</src>
## Twisted pair:
- Two insulated copper wires
- Category 5: 10 Mbps, 1 Gbps Ethernet
- Category 6: 10 Gbps
 </img>
## Coaxial cable:
- Two concentric copper conductors
- Can achieve high data transmission rates
</img>
## Coaxial cable:
- Two concentric copper conductors
- Can achieve high data transmission rates
 </src>
### Fiber optic cable:
- Glass fibre carrying light pulses representing bits
- High-speed operation:
- High-speed point-to-point transmission (e.g., 10’s-100’s Gbps transmission rate)
- Low error rate:
- Repeaters spaced far apart
- Immune to electromagnetic noise
</src>
### Fiber optic cable:
- Glass fibre carrying light pulses representing bits
- High-speed operation:
- High-speed point-to-point transmission (e.g., 10’s-100’s Gbps transmission rate)
- Low error rate:
- Repeaters spaced far apart
- Immune to electromagnetic noise
- Signal carried in electromagnetic spectrum
- No physical “wire”
- Carry a signal for long distances
- Propagation environment effects:
- Reflection
- Obstruction by objects
- Interference
Classified into 3 groups:
- Very short distance (e.g. Bluetooth)
- 5~10 metres
- LAN (e.g., WiFi)
- 10 to a few hundred meters
- Wide-area (e.g., cellular/mobile)
- Tens of miles
 </img>
</img>
- Two types of satellites for communications:
- geostationary (~36000 km above earth, stationary)
- used where DSL or cable-based access is unavailable
- low-earth orbiting (closer to earth, move over the surface)
 </src>
- Wireshark software used in the labs is an open source packet-sniffer
---
# Summary
- An overview of Networks and network components
- An overview of protocols
- Different types of physical media for data transmission in networks
- Network security
## Reference:
1. Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach [Chapter 1]
</src>
- Wireshark software used in the labs is an open source packet-sniffer
---
# Summary
- An overview of Networks and network components
- An overview of protocols
- Different types of physical media for data transmission in networks
- Network security
## Reference:
1. Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach [Chapter 1]